Or about my favourite resource in this academic year, hands down.

Ingredients
- A notebook for each student and a box to keep all the class notebooks. These notebooks don’t travel home, they live in the classroom.
- Some writing materials: pencils, markers, crayons.

Why we love it
- For all of the students in all the groups where I introduced notebooks (and that’s everybody, pre-primary, primary, juniors and teens, apart from my pre-primary level 1 and 2, who are still only 3 and 4 years old, they are going to get theirs a bit later in the year), this has become a surprisingly wonderful way to express their personality and to become even more present in the classroom. When I gave these out, many of my students of all ages were inquiring what they should write on the front page or on the cover page. I suppose it is because there might be some specific regulations at their schools regarding what needs to be and what can be written there. When I just shrugged my arms and said ‘I have no idea. It is your notebook. Write what you want‘, many of them looked at me in disbelief and then started to write some elaborate names in Russian or some made-up names and nicknames or just their names, in a variety of fonts and styles.
- Equally, the format of the note-taking is highly personalised, too. There are certain activities that we use these notes for (see below) and sometimes they involve a structure or a format which is the same to everyone but, at the same time, the kids are in charge as regards the choice of the writing materials, colours or the ratio between text and the drawings.

- It is the students’ personal space in the classroom, too. We share what we have written but I hardly ever look into those notes, unless they ask me to or unless they need help with some vocabulary or structures. Since this is a new project and since I am just developing it and discovering its potential and its potholes, I have just realised that I will have to include some kind of delayed error correction in the process, for instance by reading the entries and contributions to fish out some of the spelling or grammar mistakes.
- It give the students an opportunity to write and to read more.
- It is an opportunity to keep all the notes and all the ideas in one place and to go back to them, to review, to remember, to reminisce or to recycle.

- Notebooks for the high level students (C1) are our way of breaking into the least favourite skills ie writing. After we have finished a receptive skill task such as exam reading and exam listening, we follow it up with a 50-word (plus) summary in the notebooks, steering away from any specific genre or format, just simple note-taking that now compliment our regular ‘What do you think?’ speaking sessions. We go back to these notes in the following lessons, to check whether our views have changed in any way, whether they have developed but also, very importantly, to edit and to improve, when possible.
- Notebooks for juniors (B1) have been used in a variety of ways related to the vocabulary we study. First of all, they are the opportunity for the students to reflect on the vocabulary they have learnt. At the end of the unit, we look at all the phrases, structures and words and categorise them. The categorise we use change all the time and have included the following: easy words and difficult words, useful words and not-so-useful words, interesting words and not-so-interesting words and I am hoping to add more to this list. In the future I would also like the kids to use their own categories in the future. This kind of an activity also involves a discussion and sharing the rationale for our choices (and that is my favourite part of the whole activity). We use the notebooks also to work on the additional vocabulary, not included in the coursebook but still worth knowing. Sometimes we create the lists ourselves (ie while describing the objects, we also revised a list of materials) or we work on the lists that I prepare (ie a few weather idioms that we discussed while going through the topic of ‘extreme weather’). Last but not least, this is also where we take note of the emergent language, in the section at the end of the notebook called ‘Our special words’. I keep track of these on the whiteboard (the left margin) but I encourage the students to take a note of these (or some of these) in their notebooks.

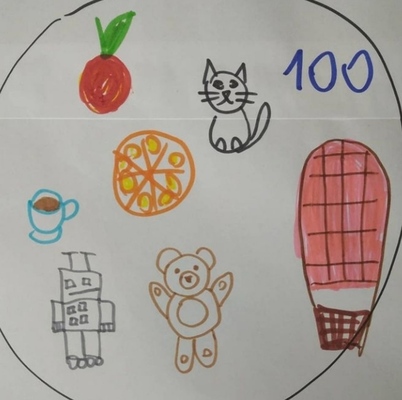
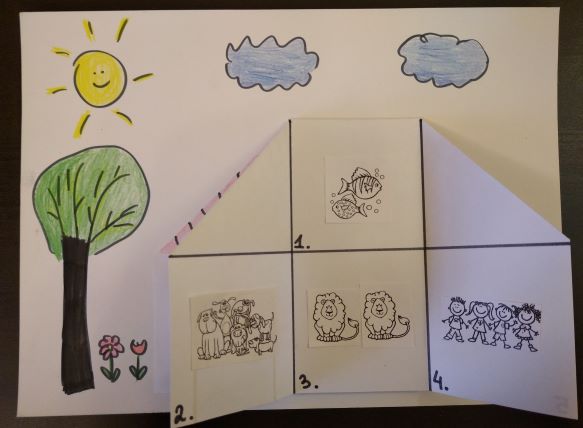
- Notebooks for primary (A2) are probably the most multi-functional among all the age groups. First of all, we use them to complete our portfolio tasks that are included in our coursebooks, one task for every two units. For these, each student gets a pre-prepared template, a notebook-page size, which they glue in and then use for whichever task we have such as the personal file (used in an interview) or the list of the adjectives to describe animals (used later in Our Big Animal Quiz) and so on. We use it also to personalise the vocabulary that we learn, for example after we have learnt the jungle vocabulary, the kids were asked to arrange all the new words in the order of their own preference, number 1 being their favourite word, number 9 being their least favourite. As with the older students, we later talked about the reasons for our arrangements. Last but not least, we use the notebooks to prepare for any student-generated games that we play. They are especially useful in all the guessing games and are much better than any small cars because the notebooks are not transparent and, because of their format, they help the kids to keep their secret words really secret. You can find out more about this game here.

- Notebooks for pre-primary (pre-A1) is a serious step towards developing reading and writing skills. Now, I am not sure whether it is going to fit all the pre-primary classes (because some children are not ready and some programme do not even include any literacy elements) but this is what works for us. My students are 5 and 6 at this point and we have been doing a lot of literacy activities for about a year now. We started relatively early simply because the kids showed interest in the written word and I realised they were ready. We went slowly but with great results and I can safely say that now it is their favourite part of the lesson. Last year we did a lot of writing on the laminated erasable pages, with whiteboard markers, this year we moved on to notebooks. We use the notebooks to copy the words that we learn, in two or three batches, with only four or five words per lesson, not to overwhelm the kids. Kids usually choose to add little drawings to these so our notebooks are slowly becoming picture dictionaries. Our notebooks are also used in pairwork, for example in a survey on the food we like and we don’t like in which the students used a pre-prepared chart (printed, cut out and glued in by the teacher) to interview their partners and to ‘take notes’ in the form of pluses and minues. I found out that the notebooks really help to set-up and to run a pair-work activity. The notebooks are also going to help us to maintain continuity with the longer-term projects such as the reading of a phonics story such as ‘A fat cat on the mat’ by Usborne and all the related activities. They will be completed over a series of lessons but thanks to the notebooks we will be able to get back to them and to revise in a more SS-centred way. Or so I am hoping.
- There is no other way of putting it is: it is a proper Notebook Love (or Тетрадка Love) and it is almost ridiculous that such a tiny and irrelevant thing, at RUB 40 a piece (about 50 cents) could have such an impact on our lessons with its potential for creativity, reflection, personalisation…And, mind you, it’s been only two months. Something tells me, the best is yet to come.

Happy teaching!
P.S. Of course I have forgotten to take proper photos in the classroom, of all the cool things in our notebooks. I will try to make up for it, at one point. For now, just some cool notebooks that are kicking about the house.
*) Тетрадка – a dimunitive of the word тетрадь (notebook)