A set of quilling paper strips
This is the second part of the Craft ABC series. You can find the first part here.
The main activity and the target language practice
This is a craft activity that features in the lesson to provide opportunities for the target langauge practice. As an example I have decided to choose our beloved jellyfish that is the first craft activity that I do with my first-year students, in one of the first weeks of the course. This is the time when we learn and practise colours with flashcards, colourful blocks and realia in general, with simple stories, videos, wordwall games and songs. A craft activity is yet another way of ‘recycling’ the target vocabulary and of giving the students an opportunity to be exposed to it and to use it.
The jellyfish is a super simple craft and even the youngest kids can draw the eyes and the smile on the head (which can be a semi-circle cut out by the teacher or a half of a paper plate) and then to attach the tentacles to the back of it. Kids are really motivated to make their own jellyfish and to drill and call out the colours and to ask for the following one, in a very simple way (‘Blue, please’). As a result, lots and lots of language is produced and everyone leaves the classroom with a creature they made herself. What’s most important, the jellyfish looks good even with the most crooked smile and the most inexpertly glued tentacles. And even if there are only three or four colours used, with the youngest kids.

The follow-up of a story or a song
Craft in this case is an opportunity to reinforce the ideas, concepts, vocabulary and structures introduced in a song or in a story. Or, to put it differently, a story or a song is not introduced only as a starter or a side dish but it becomes the topic for the entire lesson.
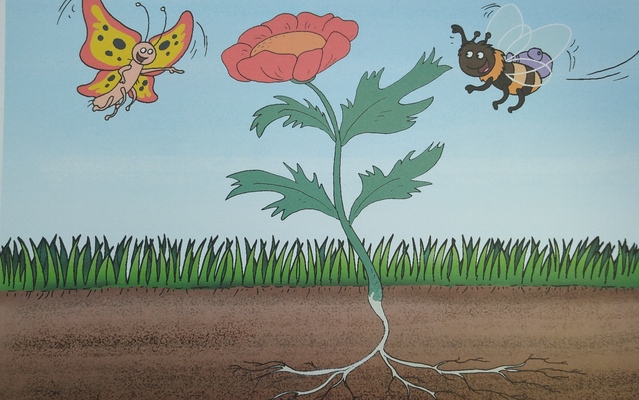
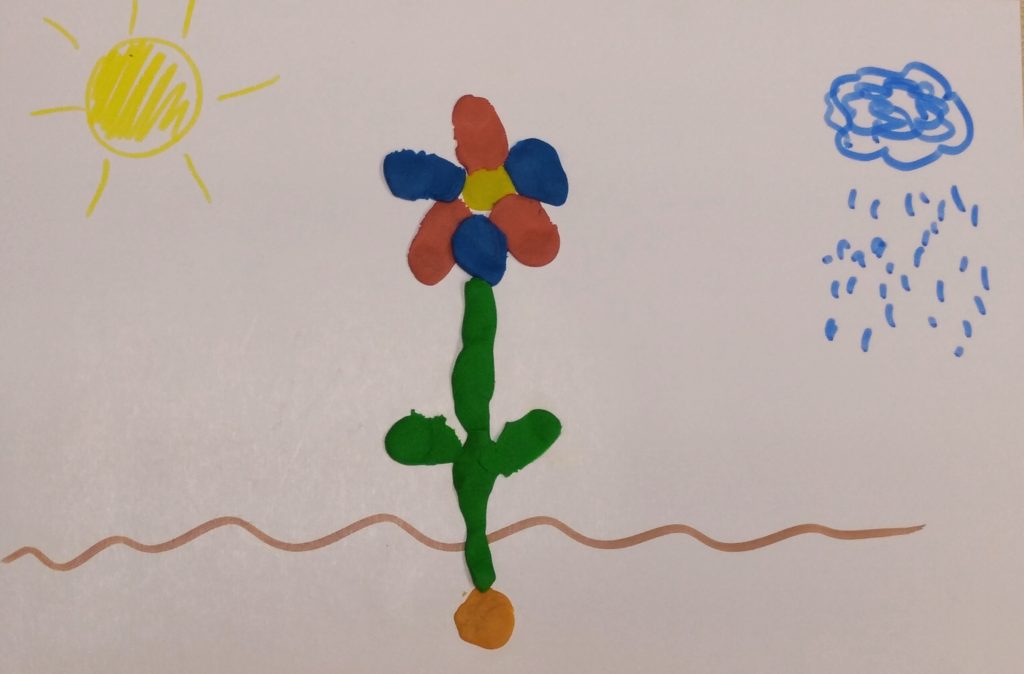
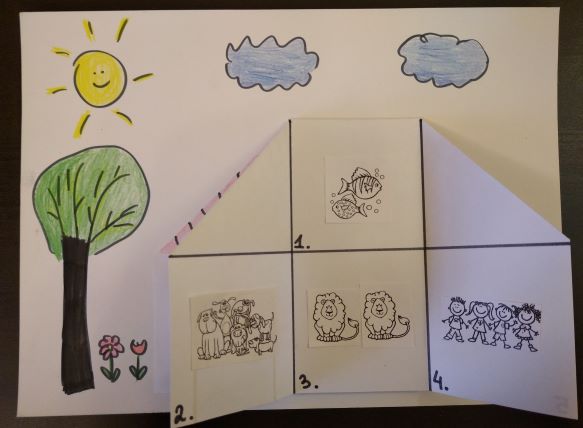
The three examples in the photos come from the lessons taught based on the Playway to English 1 by Cambridge University Press. The first one is a flower we made together while retelling the story from unit 7 (The Little Seed which you can also find here) and although we were not able to use all the original story lines, the kids could use the basic ones such as It’s sunny, It’s raining. The little seed is sleeping (at the beginning), The flower is growing (while making the stem) and so on.
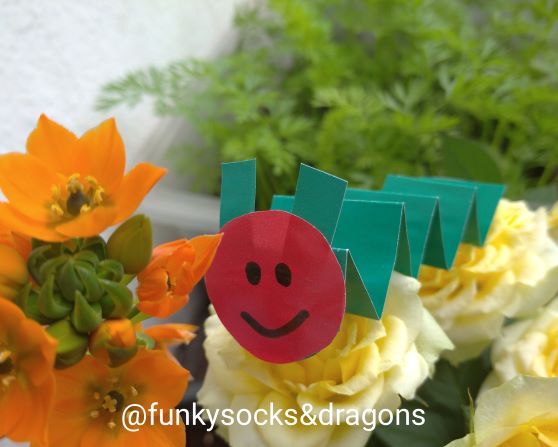
The second example is everyone’s favourite Very Hungry Caterpillar which is a storybook we use in year, to accompany either unit 7 (Weather / Spring) or unit 9 (Food). You can find more information on this version of the caterpillar here.
Last, but definitely not least, is a simple craft that was a follow-up of the amazing Super Simple Song called ‘Are you hungry?‘ and it can be used either with the topic of fruit (Playway to English 1, unit 3) as it goes nicely with the theme of the song of monsters sharing fruit with their hungry friends or, in a wider context, with food in general (Playway to English, unit 9). The craft activity becomes the more palpable and 2-D version of a song and it can be used in a mini-role play, sung or spoken, depending on what the kids are ready for.



Props preparation
This type of a craft activity does not have a lot of potential as regards maximising production although the kids are quite likely to use some functional language, the staples of craft (Are you ready? Let’s sit down, Blue, please etc). This type of a craft activity is also quite short, compared with the ones mentioned so far but that is exactly the point. The craft activity is only a prelude. Everything important is to happen later with the finished product used as a tool.
The best example here will be our magic wand. It is simple and easy to make and can be used as a part of a shapes lesson (though, really, there is only one shape involved). The abracadabra TPR activity (Abracadabra, 123, you are…) is a game we play from the very beginning of the course. When the kids are ready to take over, we make a wand for each other and use it in a game and at this point, the kids get to lead the game for real, waving their own, freshly-produced wands and we all mime whatever there is to mime. The langauge is produced and lots of it (Abracadabra, 123, you are…swimming, dancing, flying…OR you are a cat, a happy cat, a hungry dinosaur…) but it is not directly related to the making of the wand.

A part of a Science, Maths or Art lesson
Craft can be also a part of a CLIL lesson or a Maths, Science or Art lesson, depending on whether we are dealing with the EFL or the ESL or bilingual programmes. In this case, the craft activity will create an opportunity for the students to put into practice or to reinforce the real knowledge or skills they have acquired in class, making it more practical, kinesthetic and hands-on.
Below, three examples of such craft activities.
The first one is a Maths lesson in which we were learning about and practising measuring. Apart from working with the rulers and measuring tapes and checking how long our cars, teddy bears, desks, noses and fingers were, the kids also got a simple handout with a section of a certain length and it was their task to measure the strips of paper with rulers, cut of the appropriate piece and glue it underneath.
The second one is one of the lessons devoted to animal habitats which we studied in our Science class. Apart from categorising animals and talking about the habitat, we also did a craft activity in which we created the habitat (here the polar region made of a sheet of blue paper, waves drawn, ice made of cotton pats and the animals glued on). After a series of lessons we had a set of habitats.
The third piece here is one of the activities we made as part of the Kids in the Avangard. In this lesson Paul Klee was our artist of the day and we created our own version of his Cat and Bird.



The non-linguistic aims
Sometimes craft activities have a non-linguistic main aims. Because of their obvious relevance to kids’ lives and the excitement that they generate, they can be used to help kids develop as humans and this can be the reason for their inclusion in a language lesson.
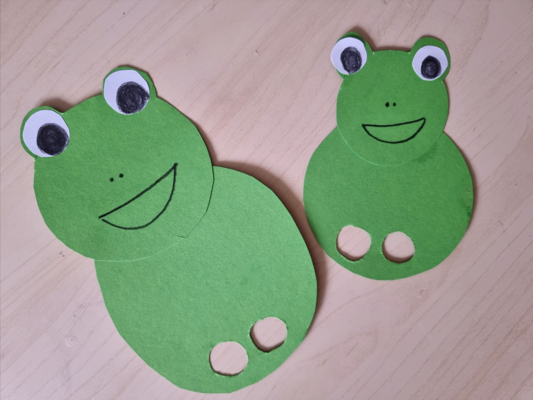
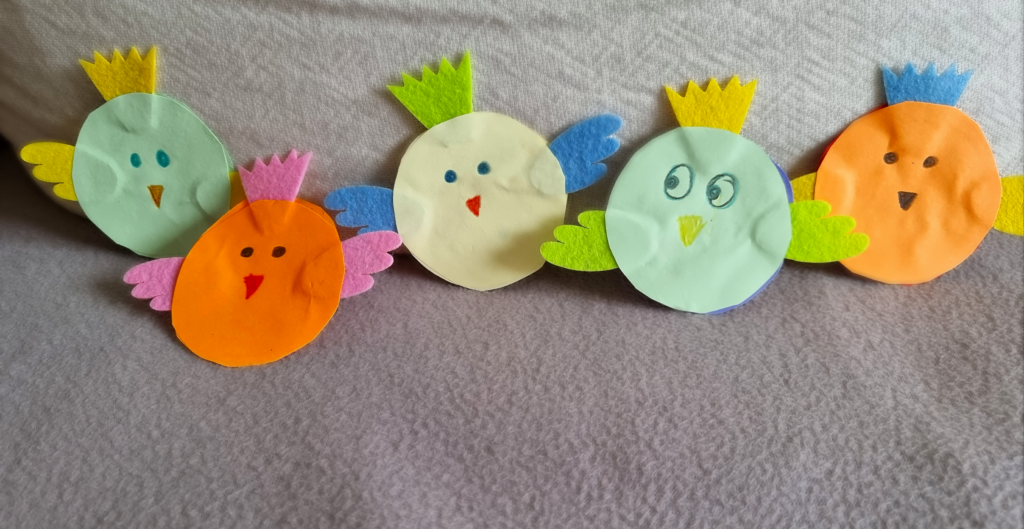
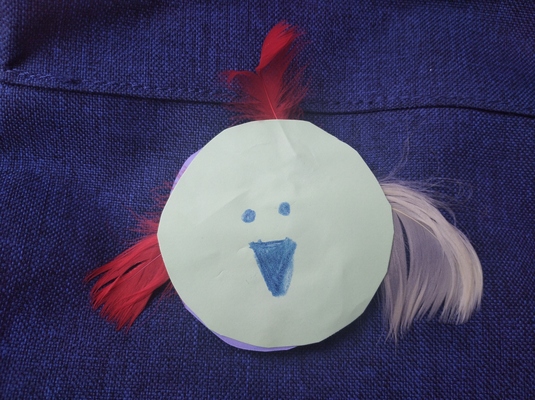
The first activity here is one of my favourite craft activities ever. It can be used in many different thematic lessons but its main advantage is that because, due to its design, it requires a detailed micro-staging and, on the one hand, it can help kids work on their ability to focus and to follow teacher’s instructions in order to be able to turn their circles into cats, dogs, frogs and bees. On the other hand (and it has worked absolutely every single time), it brings an immense sense of achievement and confidence in kids’ own skills since a random circle can become so many things.
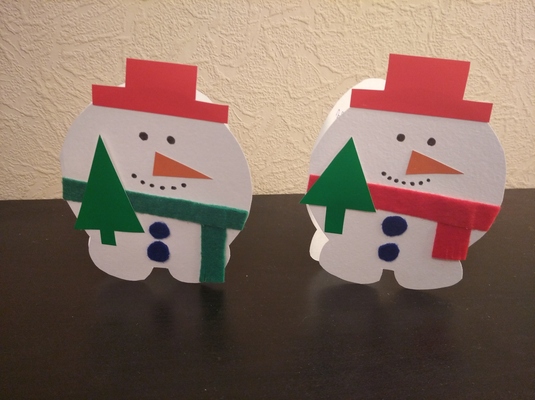
The other activity presented here is an example of a festive craft that finds its place in the classroom as part of the seasonal celebrations. Despite the fact that sometimes this vocabulary will be used in class only in a year, when the holiday comes up again, it connects the lesson to the celebrations at home and in kindergarten and it is the easiest way of bringing these festivities into the EFL classroom.
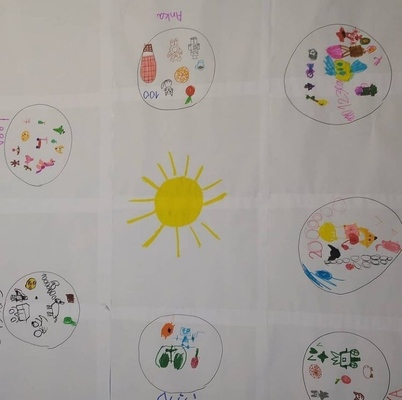
The final activity, our solar system was a wonderful activity that we all enjoyed and one that helped us produce lots and lots of language. However, believe it or not, that was not the reason why we did it. This was our first real whole class project because the kids got an opportunity to work on something together, sharing resources and sharing the space and we produced one huge poster that nobody would be taking home in the end.



Happy teaching!