Introduction
Can you hear some desperation, dear reader, in the title of this post? Rightly so. I started to write this post after one of the sessions of the summer camp that I took part in. My kids were amazing, of course, clever and eager to learn and, really, we did have a lot of fun. At the same time, looking at how they interact with each other, I could not believe my eyes and my ears. Despite the fact that many of them were already eight and nine, their social skills were on a disastrously low level. Practically anything that involved taking the other humans in the classroom into equation was a huge challenge for way too many of them. I did sigh with desperation, once and twice, and then I rolled up my sleeves and started to introduce pairwork, even though these were not my permanent students.
You may wonder why it shook me so much and why I decided to fix it. One reason is, naturally, my professional obsession with maximising production in kids and, really, I cannot imagine teaching a group of primary school children with the teacher at the centre, all the time. It is a waste of time and a waste of opportunities because kids of that age are capable of working in pairs without constant supervision. And if they do, they automatically produce more language.
However, there is more to it, of course because kids who work in pairs are more independent and more autonomous as learners and they have an opportunity to work with a variety of partners and to make friends and to bond with the group. This, in turns, is a better prognosis for the general classroom and behaviour management because you are less likely to get into trouble and to disrespect someone that you actually like and respect. If only you had a chance to get to know them and to like something about them.
Pairwork, yes or no? YES. One, big, decisive YES.

Where the angels don’t fear to tread. Pair-work in pre-school?
Yes, absolutely yes! I have been introducing pairwork in my pre-school groups first intuitively, simply because I had a very big group of children and we never got to produce any language apart from choral, whole class production and that simply was annoying for me, as the teacher. My students had a lot of potential and I did not want to waste an opportunity. Not quite knowing what to do and how to do it, I started to move towards working in pairs. It worked and by the end of the second year of pre-school, my group was ready and I was able to do what I do with my teens or adults: ‘Together, together, together’ while pointing at pairs of students. By the time we got to primary, this was a natural part of our lessons and some of the children were not even seven at this point. It is possible.
Then, naturally, I decided to do it again, with a new year 1 group, but this time, in a more conscious way, in order to be able to share it with my teachers. We started the course in September, we started to shape the group and the routine and we started to introduce pair-work. I kept my eyes open, I kept our class journal and we did it. It took 13 weeks of a course, with classes that took place only once a week. I presented the results of this research at our BKC Conference in 2020. and you can read more about it in a post here.

How to do it: The choice of the activity
The choice of the activity is one of the most important elements contributing to the success of the whole process. I got a heads-up here only because I have been teaching for many years and I had a chance to bump into one of the older coursebooks for kids which, although it had a few disadvantage and which does not even come close to the level of the currently used coursebooks for children, it did include a few ingenious solutions and, among them, the one I am going to describe below.
The one that featured in every unit of the coursebook was the maze the example of which you can see below. Initially, it was a simple but effective listening game, to practise the target language, especially vocabulary. Kids would listen to a robot dictating the path through the maze, for example: START: red…blue…yellow…brown…grey…etc until one of the exits, A, B or C. The words were separated by a funny sound, something that I would describe as ‘stomping by a robot, marching’ that the kids absolutely LOVED but it also gave them a great advantage of getting enough time to prepare for the following step. In every activity there were about 6 or 7 rounds of the game.
This game can be easily turned into a speaking – listening game and, eventually, into a pairwork.
It starts with the teacher NOT using the audio and dictating the route through the maze, with the kids following it and reaching the final destination. Naturally, the following step is the teacher nominating the students to decide on the following step, one word per child. This stage can go on for as long as it is necessary for the kids to become familiar with the format.
Afterwards, either still in the same unit and with the same maze or in the following unit with the new vocabulary, kids are put into small teams and they lead each other, in teams, through the maze. Eventually, they are put into pairs and they do it with only one partner, with one student speaking and the other student listening and following from the start to the exits.
In order to make it more monitorable, for the teacher and for the students and, also, to make it more achievable, we started to trace the route with coloured pencils or markers, each round with a different colour. This way, the children could always go back in case they got lost and the children can also monitor each other, the student dictating could potentially see where their friends were going.
This way, in a relatively short period of time, the kids got used to the new format, to working together, with only a partial monitoring and support from the teacher. It definitely helped that the vocabulary range in each case was quite limited, namely, only single words, from the obligatory set of words introduced and practised before. The students were not overwhelmed and could focus only on the format of the game. At the same time, however, in the later units of level 2, there were also more complex mazes, for example one in which the kids had to listen to a brief description of an animal for example: it has got stripes, it is big, it can run (zebra). Obviously, that means that the level of challenge can be raised when the children are ready for it.
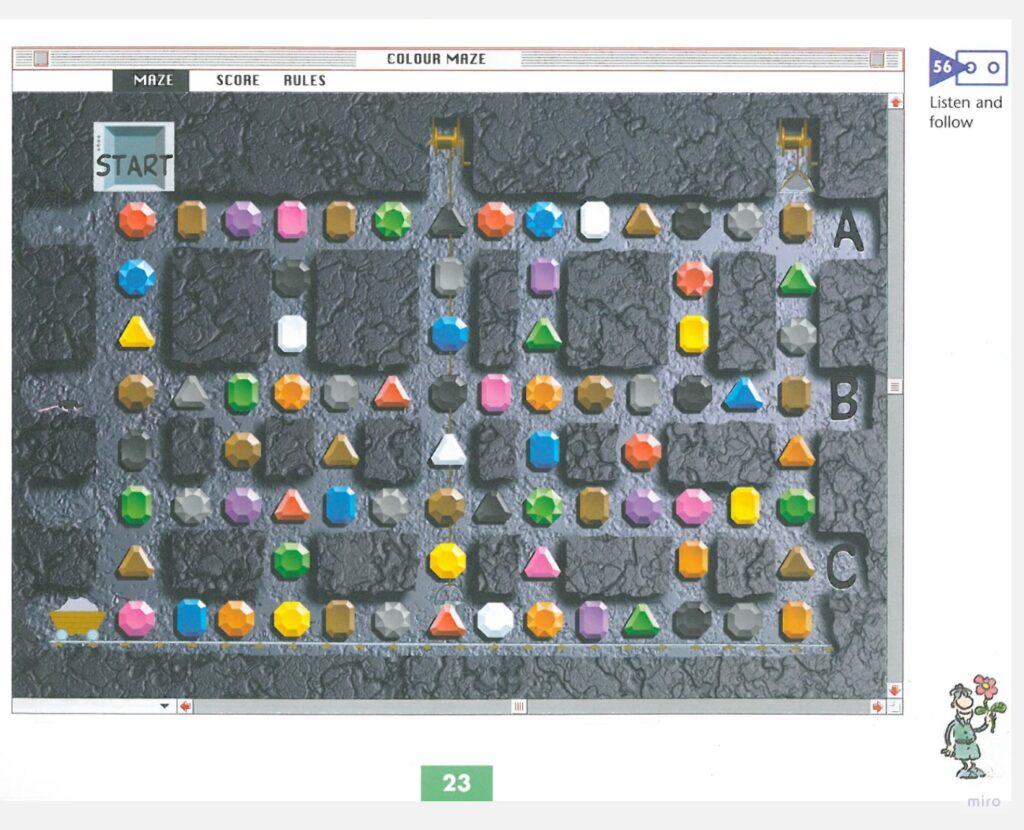
It is very easy to recreate the idea using only the black and white clipart visuals and a grid of the required size. Here you see a maze that I created for my preschoolers (rooms).

Below you can see one more type of an activity that features almost in every unit of the coursebook and this one is specifically designed for pairwork for the young students. It was always some kind of a guessing game, with the two spies (the theme of the book, duh:-) trying to guess what the other one is thinking about. I really liked it for the visuals specifically designed for that purpose and the target langauge beautifully displayed on the page to support the students’ production. Using these was a lot of fun and it was effective but I still think that the previous one, the maze, worked better as regards the first steps in working in pairs.


Contributing factors
There is a whole lot of things that a teacher can do in class in order to facilitate the whole process. They can be implemented throughout the course, little by little, bit by bit.
- Seating: make sure that the kids are sitting in a way that faciliates pair-work, in some sort of separation from the other pairs, for example by pairing up the tables and chairs, putting the chairs and kids facing each other.
- Resources: these need to be prepared with a lot of care and attention. Apart from the example based on the activity that features in the I Spy coursebooks, described above, the teacher can also use a set of mini-flashcards, as described in my post about pair-work for preschoolers. These cards are used in a game of simple riddles but the cards themselves are small (eight or six or four that fit on an A4 piece of paper) in order for the kids to be able to manipulate them with ease. What is more, a set comprises of an envelope, too that holds all the cards. This way, there is no danger of kids dropping the cards (or if they do, these will fall back into the envelope) and the secret, very necessary in that game, is easily kept throughout the game. Even if the cards are printed on a regular photocopying paper, they are not see-through, being in the envelope.
- Roles and turn-taking: Another thing is that the teacher only needs one envelope per pair. This helps a lot with assigning the role. It is crystal clear to the kids who is speaking (the child with the envelope) and who is listening (the child without the envelope). Turn-taking is also more obvious since the kids are literally passing the baton here, the envelope or whatever is the set of materials.
- Signals: Introducing the pairwork is a part of the routine and, naturally, it will take some time. To facilitate it, like with the other elements of the class routine in primary and pre-primary, it would be good to include some visual representation of the pairwork, such as gestures or chants, anything that will signal to the students what is about to be the following stage of the lesson. It can be for example a simple flashcard. I love to use a flashcard with a pair of socks for the younger kids and a two pears for the older kids who can get this pronunciation joke but a picture of two kids talking will do, too. Some more modern coursebooks have started to introduce those and that is great). Another solution can be a simple chant, for example ‘Let’s play together! Let’s play in pairs! 3…2…1’. As with all the chants, this will introduce the next stage and it will give the kids a chance to get ready or maybe even to organise themselves. The same applies to the end of the pairwork stage.
- Pairing-up: In the early stages, I would recommend a teacher-led pairing up. It is perfectly natural that in a group of children, there will be some students who will be better prepared to work in pairs early and some who will need to more time, even if all the students are of the same age or level. Based on the knowledge of the group and the individual children to end up with the most efficient pairing. This might be necessary to do over a few first lessons, later starting to experiment with some variations. I like to use a set of cards with all the kids’ names and we have a pairwork (or project) draft when we need it. The cards can be taken out of a box or a bag by the teacher or by students, too.
- Time: Thil will of course, depend on an activity but choosing an open-ended game, without an obvious grand-finale gives the teacher more freedom and flexibility to finish the game when it is best for the class, rather than having to go until the very end when some of the kids might already be getting tired and bore and when they can start losing their focus. It might be a good idea to set a timer on the phone or to choose a song as a timing tool. It is very necessary to tell the kids how long they will play for.

Happy teaching!!!
Bibliography
The Power of Play: How Fun and Games Help Children Thrive – HealthyChildren.org
3 Ways Your Child Builds Important Life Skills Through Play – HealthyChildren.org
Why children need to play with their friends as soon as they can (theconversation.com)
Playing Well with Peers Means Better Mental Health (verywellmind.com)