Set-up: a set of small chairs in a circle, in one super cozy corner of the classroom. This is where always start the lesson before we move to the serious part of the classroom and the lesson, with big tables, big chairs and coursebooks.
Time: 5 – 10 minutes in the beginning of each lesson
Materials: Angelina, dice and any visuals, especially flashcards, EFL posters (and at the school we do have a big and the most random collection of these from long-forgotten publishers and coursebooks), Starters, Movers and Flyers wordlist picturebooks which you can be easily downloaded (although we are lucky to have a few paper copies, too) and sometimes a whiteboard or a set of mini-whiteboards
Interaction patterns: all the new activities are first tried and tested with the whole group, to support production and to make sure that all students feel comfortable to be creative and to share their ideas. Later on, we split and continue in pairs or in teams.
Here a confession: ideally, of course, all of the interaction should be taking place in pairs to ensure that everyone has a go and produces as much language as possible but it is not what we always do. I have noticed that first of all, the children really do enjoy the whole group discussion, when everyone can contribute and when we do something together. I cannot quite describe it but it is almost palpable, this ‘team spirit’ and it does have a positive impact on them and on the atmosphere in the group. Plus, they are always curious about everyone else’s creative (aka crazy) ideas so they pause to eavesdrop, especially when there are giggles coming up from different parts of the circle. Because of that, we do both, a lot of whole class and a lot of pairwork.
Some of the activities to use in the Speaking Circle:
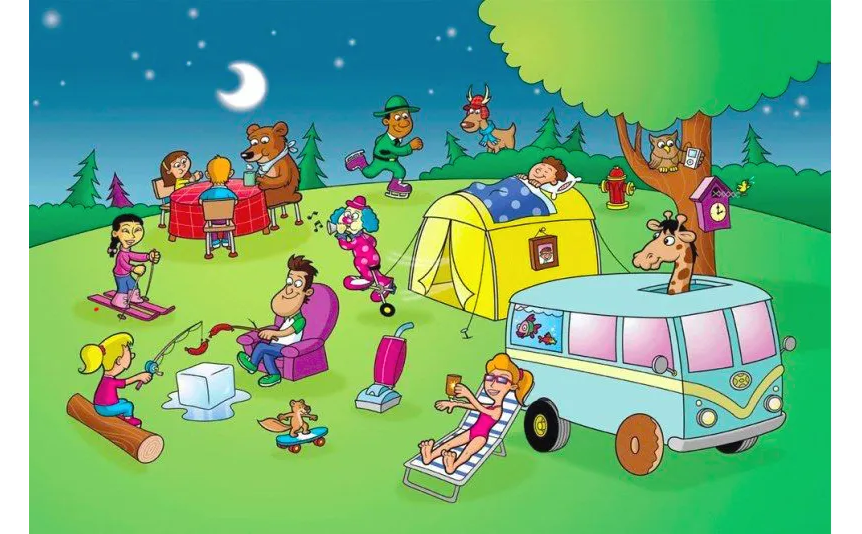
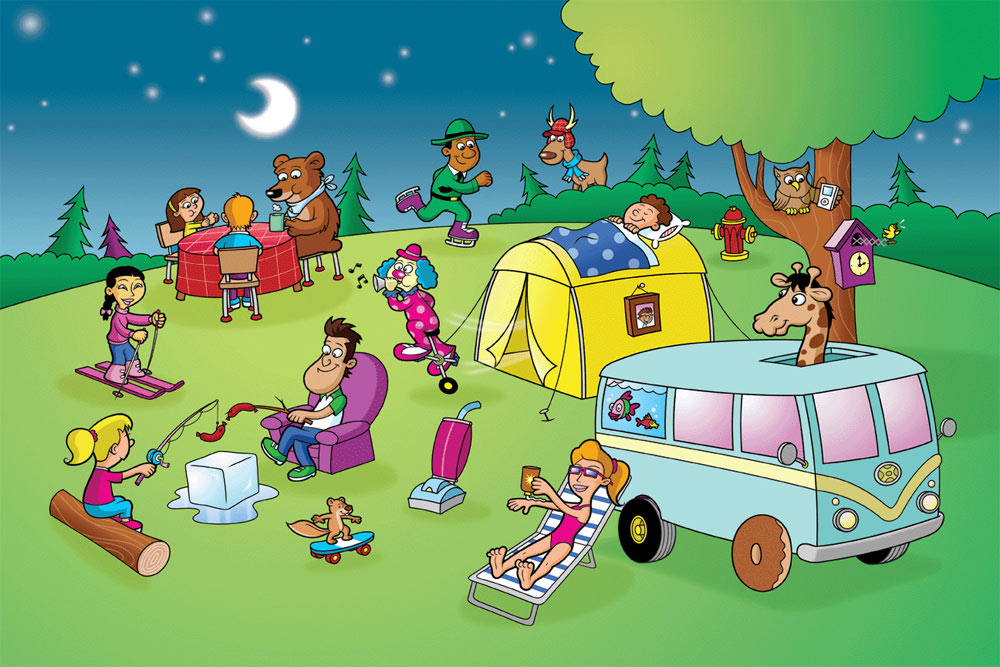
- Tell me about that boy: the kids choose a person, an animal, a character or an object in the picture. The kids choose themselves what they want to conversation to be about and what information to include. The basic information usually includes emotions, clothes, activities or location.
- Yes or no: the kids use the picture as the basis to make true or false sentences about the picture. The other students listen and correct the sentences when necessary.
- Riddles: the kids describe something in the picture (the colour, the size, the location and the activities) for the others to guess
- Which one is better?: the kids draw two cards out of the pile (animals, gadgets, food or anything else that we are studying) and they choose which one is better.
- It’s a pair: the kids look for associations among different objects, people, animals in the set and they have to explain why they have put them together
- Silly pictures: the kids talk about different silly things they see in the pictures
- Silly stories: the kids come up with a character and they take turns in coming up with the adventures based on the set of verbs and / or other words that the teacher prepares in advance (displayed on the whiteboard or on the mini-whiteboards).
- Angelina: the kids chat with the class puppet, ask and answer questions (pre-primary groups)
- Hello dice: a new variation of the hello circle that can be introduced long before the kids actually study the Past Simple. They roll the dice, once, in turns and talk about their day, starting with the key phrase and we try to encourage including justification (‘School was easy because I have only 4 lessons on Tuesday’) or evaluation (‘I ate soup and it was very yummy’) etc. Sometimes we also play with the imaginary dice which basically means that everyone can choose what they want to talk about. Somehow, then number 6 is the most common choice. Perhaps because it is most generative of all of them and it is fun to say that ‘I didn’t go to Mars’, ‘I didn’t eat a fox’, ‘I didn’t dance in the park’ and what not. Not to mention that they just LOVE rolling the imaginary dice.

Why we like it
- The kids love it
- They are very creative, they have great ideas and they want to share them
- By being creative, they also develop their creativity, there are new ideas, new approaches and even more fun
- Endless opportunities for revising without focusing too much on any specific vocabulary or structures.
- Some potential for accidental learning and emerging vocabulary (although to make it work properly, I should start keeping track of it)
- The activities do provide lots of opportunities for spontaneous (or almost spontaneous) language production where the only scaffolding devices are just the resources prepared by the teacher for the day and the langauge that the kids have at their disposal and, in many ways, we are just having a chat, despite being only A1 level.
- Really, the part of the lesson that I really look forward to, every Tuesday and every Thursday.
Happy teaching!