This is not going to be a post on the advantages and disadvantages of using a rewards’ chart in the EFL classroom. If you are interested in one or the other, please, scroll down to the bibliography with some pieces to read.
Instead, I am going to tell you a story about a period of six years of using a rewards chart with my kids, successfully and where it has got me. Or where it got us. Consider it a case study.
The group
There are eight of us, in the group, one of me, two boys and five girls and at this point (January 2021), we are in our sixth level together. On the one hand, it is a bit scary, that so much time has passed and so quickly, too, on the other hand – six levels together, pretty much with the same children, from the first words, literally, to Movers.
The first rewards chart
Once upon a time, when my kids were still very very young, in our first year together, the day came when I realised that I needed a rewards chart, badly, with a set of rules and a system.
To be honest, it was a bit of a heartbreak and it did feel like a total defeat. Until then, I had never (as in: NEVER) had to resort to it with children so young. Not once in my entire teaching career (of 10+ years). Rewards charts were for the primary and teens, not for the babies. Sigh.
I was thinking and pondering and wondering, approaching it with a lot of trepidation (in Polish we say: to come up to something like a dog to a hedgehog) and really, stubbornly, putting off the D-day. But, the group was a big one, with ten kids, some of whom were six, some of whom were barely three and they were just rowdy (even for my standards) and ‘my traditional methods’ (or whatever they were back then) were just not working. As in: at all.
Reluctantly and very un-enthusiastically, I took a deep breath and introduced changes: a set of rules and a rewards chart.
The class rules: How to.
- Think of your group, the kids sitting in your classroom. What are they struggling with? What is the unwanted behaviour right here, right now? Choose the most important three behaviours that you would like to eliminate. There is no point in constructing a set of ten commandments as there will be too many to revise, to remember and to focus on.
- Formulate the rules and try not to use negatives. ‘Sit nicely’ sounds much better and is more positive than ‘Don’t run’.
- Yes, there might be situations when a clearly formulated ‘Don’t‘ is the only solution. In the group that I am describing here, we did have some issues that the kids decided to resolve with fighting so for some time, this was our rule number 1.
- In general, it would be better to refrain from using imperatives altogether and go for full sentences, for example, instead of ‘Sit nicely’ we were using ‘I sit nicely’, together with ‘I don’t run’, ‘I listen to the teacher’, ‘I don’t fight’. These are great language models and, over time, they become a part of everything that the kids can say, even early on, in the first year of primary or pre-primary. Investing in the rules is also investing in the language.
- Think how you will introduce the rules. I prepared A4 flashcards, with the rule written down (for me to remember and to be consistent and for the kids, to expose them to the written word, although, of course, back then they were not able to read these), with an appropriate picture (thank you, clip art) and with an accompanying gesture for each of them.
- The first time I introduced them slowly, using the gestures, drawing the kids attention to the pictures and repeating the rules a few times. They did get the idea pretty quickly. After all, they learnt how to behave and how not to behave. After all, they are familiar with the concept of rules. They are rules in the kindergarten, in the art classes, at the swimming pool. Naturally, there will be some in their English class, too.
- How was I sure that they did understand? Because, of course, one brave volunteer quickly translated them into Russian and all the kids started to discuss the rules. I went over the rules a few times and I encouraged the kids to repeat the gestures.
- Put the posters up, in a place where everyone can see them. In my case, the best place for that was the door, on the classroom side:-)
- Revise the rules in the beginning of every lesson. I would go over the rules, ‘reading’ them out loud, while pointing at the sentences and later, once more, I would ICQ everyone, this time with gestures. ‘Do we sit nicely?‘ ‘Do we fight?‘ and so on.
- Keep an eye on your students and when a rule becomes redundant (because, hey, it worked and your students’ behaviour has improved), change it or replace it with something that is necessary and relevant at the moment.
- In our case, in the first year, after a while we could replace ‘I don’t fight‘ with a very general but also very broad ‘I am a good friend‘ which we used to signal that we basically behave well because a good friend will not fight, will not take someone else’s pencils or books, will not say unkind things about other children and will not always try to go first and so on.
- It is also good to have a rule that models and acknowledges the behaviour that is even better than good, something exceptional that we all should strive for. In our case, it was the rule number 4 ‘I am fantastic‘ which I chose because it sounds similar to its Russian equivalent and it is a positive word.
- Make sure that you refer to the rules throughout the lesson, to remind the students about them when you notice some examples of the unwanted behaviour. I do it using a question form, while using the gesture or pointing at the posters, for example ‘Are you a good friend?‘, ‘Are you fantastic?‘, ‘Are you sitting nicely?‘

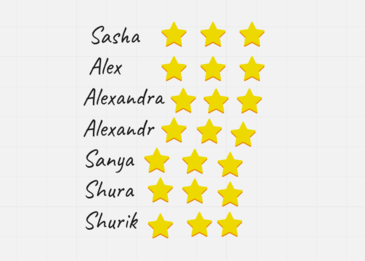
The rewards’ chart. How to. A case study.
- I decided not to use the board as it was too far away from our little circle and I did not want to get up and walk away from the kids a few times during the lesson as it would be too disruptive. Instead, I got a clipboard and prepared a table with their names, written in different colours and accompanied by little icons, ten different ones, so that the kids, who were pre-literate at the time, could recognise their names easily. I put the table into a plastic sleeve, sealed it and pronto. Laminating it would do the job, too. I used a whiteboard marker and so I could easily clean it and re-use it in the following lesson. I was also able to carry it around the classroom.
- A few times during the lesson, I would take out the chart and check out, with all the kids, asking everyone the same question ‘Are you fantastic?’ (or any other question relevant to our rules, but this one was the most common one) and, if they answered ‘yes’, I would add one more star to the chart, next to their names.
- Naturally, if the student did seriously ‘misbehave’ (inverted commas here because it really does happen rarely), first would come a warning and then, possibly, if that didn’t work – a tiny little bit of a star might get erased. Which happened on a few occasions and usually the warning itself was enough.
- In the beginning, I did do it after every single stage and almost after every single activity. It did take time but it was worth it. With time, I was able to cut down on the frequency and the number of stars, extending the length of the stage that could earn them a star.
- Eventually, we got to the point when each child would get only one star at the beginning of the lesson. It was their job to make sure that it stays whole until the end of the lesson.
- There was also a point, in year two, when we started to invest more time into our stars because at the same time, we started to talk about other people, and the stars gave us a perfect opportunity to do just that, ‘My star is…’, ‘My star has got…’ and, of course, it was then even more important to keep all the stars intact.
- It is also very important to remember that the kids should be given an opportunity to get better and to be acknowledged when their behaviour improves. It should not be a problem since the teacher is in charge of when the new stars are awarded.
- Also, whenever we ask the question ‘Are you fantastic?’, I always start from the well-behaved students, mainly in order to give the ‘not-so-fantasic’ ones a chance to calm down and to think about life so that, when it is their turn, they could be ready to be fantastic, too.
- ‘Are you fantastic?’ is a very powerful question in itself, too. On the one hand, it serves as a reminder of our aim and our rule (‘We are fantastic’), on the other hand, it is another chance for the students to confirm that they are fantastic AND to make a conscious decision and to make a promise that yes, they will be, from now on, even if there have been a few issues with it.
- Eventually, by the time we got to our level 3, the rewards chart became almost completely unnecessary. We had the rules on the wall (a new classroom) and I still kept the rewards chart grid at the ready but I would only take it out and use it, when someone needed a reminder that we are, in fact, fantastic. Which, in year 3, happened perhaps once a month.
Today aka the Outcomes
Today, in our 6th year together, we have long forgotten about the rewards’ chart and the rules. My students are now seven, eight and nine and, after all this time, it is no longer necessary to keep such a strict routine and such an elaborate system. The last time we did come close to anything resembling a rewards chart was a collage (an example of which you can see in the photo above), which we made on our Miro board, at the end of each lesson. Everyone could choose an image, google or icons, that they wanted to add. This, in a way, was some kind of a reward for everyone.
Looking back, I think it was a good decision, to introduce the chart and the rules all these years ago and even a better decision to ‘waste’ time on drawing all these stars and asking all these questions. And, dear teacher, if you worry that it takes six years to reap what you sow, don’t. The effort made and the time spent did start to pay off already after a few weeks.
I cannot guarantee that we are going to stay in that bliss forever (fingers crossed that I don’t jinx it with this post) but so far, so good.
My kids have never been very quiet (apparently it’s because I am loud, I am told) but they do behave. Today, after all these years, we all know what is OK and what is not. Most of the time, that is.
They have become more talkative and for that reason a new ‘poster’ appeared on the noticeboard. ‘When I speak, people listen. When people speak, I listen’. It works. Especially that we did specify that by ‘people’ I mean both, teachers and students present in the classroom.
On some days, I have to bring Pasha, our invisible student, one some days I call them using their first name, in full, and their patronymic, sometimes I have to use my serious face but that’s it. I want to believe that it all started with a simple rewards chart a long, long time ago…

Happy teaching!
Something else to read
- Rewards charts: how to use them to change the child behaviour at raisingchildren.net.au
- Are rewards charts actually bad for our kids? at healthymummy.com
- Why you shouldn’t reward kids all the time? at sleepingshouldbeeasy.com
- Rewards for kids: Maybe all they want is time? at kiddycharts.com
- 20 classroom rewards to get students motivated at englishteaching101.com
5 thoughts on “Rewards charts and young learners”